
They connect the motor to ground (negative terminal of the battery). Schematic of a bipolar transistor hbridge circuit to drive a DC motor.Ĭan you see the letter 'H'? There are many different ways to draw the circuitry, but the above wiring diagram matches the model of most h-bridges. The H-bridge circuit (below) looks complicated at first glance, but it is really just four copies of a resistor + transistor + diode.

In later pages, I'll compare the performance of three different part numbers of popular transistors (2N3904/2N3906 vs 2N2222A/2N2907A vs Zetex ZTX1049A/ZTX968) using a common robot motor from. This H-bridge can operate from a power source as low as two nearly-exhausted 'AAA' batteries (2.2V) all the way up to a fresh 9V battery (9.6V). That is, an H-bridge allows a microcontroller, logic chip, or remote control to electronically command the motor to go forward, reverse, brake, and coast.įor the purposes of this article, I’m focusing on a basic H-bridge that is a good choice for most robots (including BEAM robots) and portable gadgets. An H-bridge is an arrangement of transistors that allows a circuit full control over a standard electric DC motor. H-Bridge Motor Driver Using Bipolar Transistors The classic beginner’s DC motor driver circuit that appears in every electronics textbook is the bipolar transistor H-bridge. The light dependant resistor (LDR or CdS since the sensor is made of. The sensors are cross-wired to the opposite motor's transistor gate.
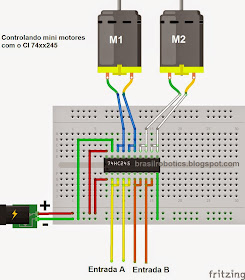

The light sensor for the right motor is on the left, and the light sensor for the left motor is on the right. Light-chasing robot kit with functional whisker and tail sensors! This is the circuit diagram for the light sensitive motor driver.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
